Antibody
| Name | Vitamin B12 Antibody (VB12 Antibody) | ||
| Catalog No. | H835e1 | ||
| Clonality | Monoclonal | ||
| Host | Rabbit | ||
| Reactive Species | Human | ||
| Application | CLIA(AE) | CLIA(ALP) | ICA |
| C1770 (Capture) - H835e1 (Detection) | H835e1 (Capture) - C1716 (Detection) | H835e1 (Capture) - C1750 (Detection) | |
| Purity | Protein A/G Purified, Purity >95% | ||
| Storage Buffer | 1xPBS,pH 7.4 | ||
| Storage Instructions | Upon delivery aliquot and store at -20°C. Avoid freeze / thaw cycles. | ||
Antigen
| Name | Intrinsic Factor (IF) | ||
| Catalog No. | C1716 | C1750 | C1770 |
| Species | Swine | ||
| Type | Recombinant | ||
| Tag | His | ||
| Expression System | Eukaryotic cell | ||
| SDS-PAGE |  |
 |
 |
| Purity | >90% (R250-stained SDS-PAGE) | ||
| Storage Buffer | 1xPBS,pH7.4 | ||
| Storage Instructions | Store at -80°C in aliquots. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles. | ||
CLIA Bulk Reagent
| Name | Catalog No. | Recommended Platform | Methodology |
| Vitamin B12 (VB12) Bulk Reagent | Q801a1 | CLIA(AE) | Sandwich Assay |
| Q801a2 | CLIA(ALP) |

Nanjing OkayBio launches its innovative Vitamin B12 (VB12) sandwich assay series, featuring a groundbreaking 3-component chemiluminescent immunoassay(CLIA) bulk reagent. This advancement streamlines traditional 5-component systems, reducing detection time by 30% through optimized reaction protocols. Validated on CLIA platforms, the reagent achieves a sensitivity of 5 pg/mL and demonstrates exceptional correlation (R² >0.95) with Roche-assigned samples.

Product Data
VB12 antibody (H835e1) and intrinsic factor (C1770) were used to detect VB12 samples (0–2000 pg/mL).
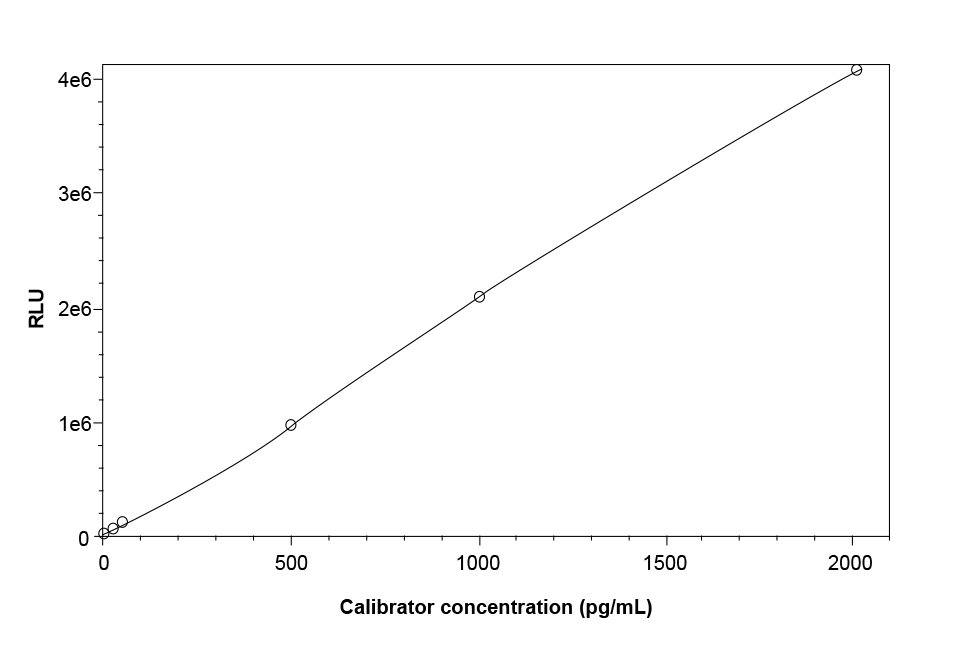
Figure 1. VB12 Calibration Curve
| Sample | Concentration (pg/mL) | RLU |
| 1 | 0.0 | 8308 |
| 2 | 22.2 | 64128 |
| 3 | 52.3 | 109666 |
| 4 | 499.5 | 957793 |
| 5 | 1004.1 | 2084186 |
| 6 | 2015.4 | 4067850 |
Table 1. VB12 Calibration Curve Data
Roche-assigned samples (35.1–1934 pg/mL, n=48 ) tested with H835e1 and C1770 showed R² = 0.9926.
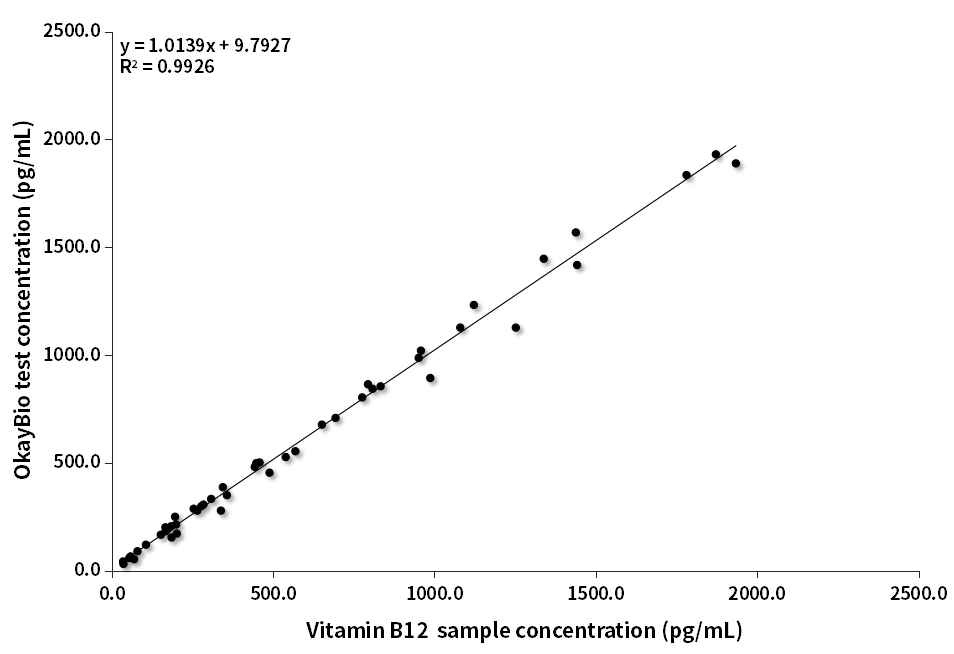
Figure 2. VB12 Sample Concordance
(Roche-assigned)
| Sample | Assigned Conc.(pg/mL) |
Detected Conc.(pg/mL) |
| 1 | 35.1 | 43.8 |
| 2 | 36.2 | 32.4 |
| 3 | 54.3 | 59.8 |
| ︙ | ︙ | ︙ |
| 47 | 1872 | 1931 |
| 48 | 1934 | 1889 |
Table 2. VB12 Sample Concordance Data
(Roche-assigned)
| Calibrator | Concentration (pg/mL) | RLU Mean | Linear Equation |
| S1 | 0 | 8308 | y=2514.4x+8308 |
| S2 | 22.2 | 64128 | |
| Mean RLU values of zero - conc. diluent measured 20 times | 8701 | ||
| SD | 427.7 | ||
| Mean +2SD | 9556 | ||
| LoD (pg/mL) | 0.496 | ||
Table 3. Limit of Detection of VB12
Antigens (VB12, Adenosylcobalamin [AdoCbl], Hydroxocobalamin [HOCbl], and Methylcobalamin [MeCbl]) were diluted to 500 and 2000 pg/mL in 10mM PBS for detection.
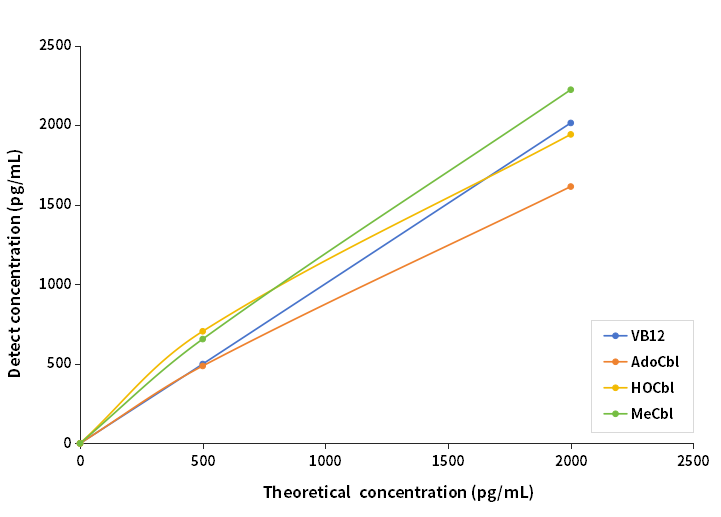
Figure 3. Specificity of VB12 Antibody Recognition
| Theoretical Conc.(pg/mL) | Detected Conc.(pg/mL) | |||
| VB12 | AdoCbl | HOCbl | MeCbl | |
| 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 500 | 499 | 487 | 705 | 656 |
| 2000 | 2015 | 1615 | 1943 | 2224 |
Table 4. Specificity of VB12 Antibody Recognition Data
The same batch of VB12 antibody (H835e1) and intrinsic factor (C1770) were used to detect Roche-assigned samples at concentrations of 50.26 pg/mL and 523.7 pg/mL 10 times each. The measured concentrations exhibited coefficients of variation (CV) of < 3% for both low- and high-value samples.
| Low-Concentration Samples | ||
| Sample | RLU | Concentration (pg/mL) |
| 1 | 107100 | 50.26 |
| 2 | 107866 | 50.87 |
| 3 | 107502 | 50.58 |
| 4 | 107213 | 50.35 |
| 5 | 107112 | 50.27 |
| 6 | 108017 | 50.99 |
| 7 | 106987 | 50.17 |
| 8 | 106547 | 49.82 |
| 9 | 104710 | 48.36 |
| 10 | 108306 | 51.22 |
| Mean | 107136 | 50.29 |
| SD | / | 0.80 |
| CV | 1.6% | |
Table 5. VB12 Detection Repeatability
(Low-Concentration)
| High-Concentration Samples | ||
| Sample | RLU | Concentration (pg/mL) |
| 1 | 991892 | 514.2 |
| 2 | 1010307 | 522.4 |
| 3 | 1003793 | 519.5 |
| 4 | 1037952 | 534.7 |
| 5 | 1009633 | 522.1 |
| 6 | 1074624 | 551.0 |
| 7 | 1041325 | 536.2 |
| 8 | 986505 | 511.8 |
| 9 | 1026037 | 529.4 |
| 10 | 1033005 | 532.5 |
| Mean | 1021507 | 527.4 |
| SD | / | 11.79 |
| CV | 2.2% | |
Table 6. VB12 Detection Repeatability
(High-Concentration)
Free Sample Application
Item Introduction
Vitamin B12 is the collective term for a number of substances with qualitatively equivalent biological effects. These compounds consist of a corrin ring system that is similar to porphyrin with four reduced pyrrole rings and a central cobalt ion and are therefore referred to as cobalamins. Characteristically, all cobalamins have an α-axial ligand at the cobalt ion consisting of a phosphoribosyl-5,6-dimethylbenzimidazole side chain. The β-axial position can be occupied by various substituents. Depending on the group (R), a distinction is made between cyano- (R = CN), aquo-(R = H2O), hydroxo- (R = OH), methyl- (R = CH3), and adenosyl-(R = 5’-deoxyadenosyl) cobalamin. Cobalamins are synthesized only by microorganisms, and humans and animals receive them solely through the food chain. In natural foods, vitamin B12 is present mainly as hydroxocobalamin and adenosylcobalamin and is found in milk as methylcobalamin. Due to its stability, cyanocobalamin is used in fortified foods as well as in pharmaceuticals and dietary supplements. Some pharmaceuticals and dietary supplements also contain hydroxocobalamin and methylcobalamin.
Vitamin B12 is necessary for the transformation of methyltetrahydrofolate to tetrahydrofolate for DNA synthesis. B12 deficiency can therefore lead to functional folate deficiency and impaired DNA synthesis, resulting in pernicious (megaloblastic) anaemia.
